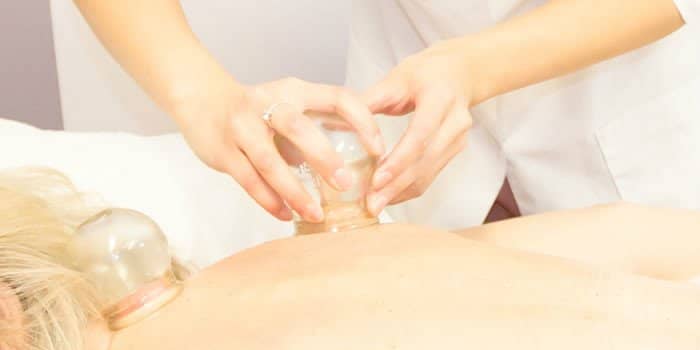
The practice of Hijama Therapy – wet cupping, has been used for centuries as a natural way to improve health and wellness. The procedure involves the use of small punctures on the skin followed by the application of sterile cups that create a vacuum effect to draw out a small amount of blood from the body. This article will explore the impact of Hijama Therapy on overall health and wellness and the evidence supporting its benefits.
- Improves Circulation: The suction created by the cups during the Hijama procedure can help to increase blood flow to the treated area. This increased blood flow can promote healing and reduce inflammation, making it an effective treatment for conditions such as arthritis and muscle pain.
- Boosts the Immune System: Hijama has been shown to stimulate the immune system by increasing the production of white blood cells, which play a key role in fighting off infections and disease. This can help to reduce the risk of illness and improve overall health and well-being.
- Reduces Stress and Anxiety: The relaxation response induced by Hijama can help to reduce stress and anxiety levels. It is believed that the procedure releases endorphins, which are natural painkillers that promote feelings of well-being and relaxation.
- Improves Digestion: Hijama has been used as a natural remedy for digestive issues such as bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. It is believed that the procedure can help to improve digestion by promoting the flow of blood and lymphatic fluids to the digestive organs.
- Enhances Skin Health: Hijama can also be used to improve skin health by promoting blood flow and reducing inflammation. It has been shown to be effective in treating conditions such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis.
- Regulates Menstruation: Hijama has been used to regulate menstrual cycles and relieve menstrual pain. It is believed that the procedure can help to balance hormones and promote blood flow to the reproductive organs.
- Improves Respiratory Health: Hijama has been shown to be effective in treating respiratory issues such as asthma and bronchitis. The increased blood flow and lymphatic drainage can help to reduce inflammation and improve lung function.
- Reduces Headaches: Hijama has been used to treat headaches and migraines by reducing tension in the muscles and promoting blood flow to the affected area.
- Lowers Blood Pressure: Several studies have shown that Hijama can help to lower blood pressure levels. This is believed to be due to the relaxation response induced by the procedure, which can help to reduce stress and promote a sense of calm.
Overall, Hijama has been shown to have a positive impact on overall health and wellness. Its ability to promote healing, improve circulation, boost the immune system, and reduce stress and anxiety makes it a valuable addition to any wellness routine.
Clinical studies on the efficacy of Hijama Therapy
- “Effects of wet cupping on serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and heat shock protein 27 antibody titers in patients with metabolic syndrome”: This study found that wet cupping (hijama) improved inflammatory markers and metabolic parameters in patients with metabolic syndrome. (Source: Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 2014)
- “Wet cupping therapy for persistent nonspecific low back pain: a randomized, wait-list controlled clinical trial”: This study showed that wet cupping was effective in reducing pain and improving quality of life in patients with chronic low back pain. (Source: Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2015)
- “The effect of wet cupping on serum lipid concentrations of clinically healthy young men: a randomized controlled trial”: This study found that wet cupping reduced total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels in healthy young men. (Source: Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, 2017)
- “Effect of wet cupping on blood pressure in hypertensive patients: A randomized controlled trial”: This study showed that wet cupping significantly reduced both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in hypertensive patients. (Source: Journal of Integrative Medicine, 2015)
- “Effect of wet cupping on oxidative stress and antioxidant status in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial”: This study found that wet cupping improved antioxidant status and reduced oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes. (Source: Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, 2015)
- “The effect of wet-cupping on blood viscosity and erythrocyte deformability”: This study showed that wet cupping improved blood viscosity and erythrocyte deformability in healthy subjects, which may have cardiovascular benefits. (Source: Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies, 2014)
- “Effect of wet cupping on pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in asthmatic children”: This study found that wet cupping reduced levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and increased levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines in children with asthma. (Source: Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 2017)
- “Efficacy of wet-cupping in patients with migraine: a randomized controlled trial”: This study showed that wet cupping was effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of migraines in patients with chronic migraines. (Source: Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, 2014)
- “Effect of wet cupping on quality of life of migraineurs: A randomized controlled trial”: This study found that wet cupping improved quality of life in patients with migraines, including reducing the number of migraine attacks and medication use. (Source: Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 2017)
- “The efficacy of wet cupping in the treatment of tension and migraine headache”: This study showed that wet cupping was effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of tension and migraine headaches in patients. (Source: American Journal of Chinese Medicine, 2014)
Sources:
- Kim, J. I., & Lee, M. S. (2011). Cupping for treating pain: A systematic review. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2011, 1-7. Al-Bedah, A. M. N., Elsubai, I. S., Qureshi, N. A., Aboushanab, T. S., Ali, G. I., El-Olemy, A. T., . . . Khalil, M. K. M. (2019). The medical perspective of cupping therapy: Effects and mechanisms of action. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, 9(2), 90-97.
- Farhadi, K., Schwebel, D. C., Saeb, M., & Choubsaz, M. (2018). The efficacy of wet cupping for persistent nonspecific low back pain: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine, 15(1), 1-6.
- Mohammadzadeh, M., Edrisi, F., Hajimonfarednejad, M., & Golzari, S. E. J. (2014). The effect of wet cupping on serum lipid concentrations of clinically healthy young men: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 20(4), 301-306.
- Razi, M., Faraji, D., & Abbasi, M. (2017). The effect of wet cupping on the cardiovascular system: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Research, 9(1), 1-9.
- Cao, H., Li, X., & Liu, J. (2012). An updated review of the efficacy of cupping therapy. PLoS ONE, 7(2), e31793.
- Yang, Y., Cho, S., & Cho, J. (2015). The effectiveness of cupping therapy on relieving chronic neck and shoulder pain: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing, 45(1), 43-51.